Policies are an essential part of the Cisco SD-WAN solution. They serve as the mechanism through which administrators encode their intent into the network fabric. These policies allow organizations to design traffic pattern/actions as per various requirements.
Here are some key points about Cisco SD-WAN policies:
- Business Intent Encoding: Policies enable administrators to translate business intentions into actionable rules within the network. Whether it’s optimizing application performance, reducing costs, or ensuring security, policies play a pivotal role.
- Cost Reduction and WAN Optimization: One common objective is to reduce WAN transport infrastructure costs. Achieving this often involves transitioning from an Active/Standby design to a forwarding architecture where all available links can be utilized in parallel. Additionally, organizations are moving away from expensive leased-line transports and embracing more cost-effective commodity Internet circuits.
- Application Experience: Despite these changes, business stakeholders still expect a consistent application experience. Whether it’s video conferencing, file sharing, or real-time collaboration, policies ensure that applications perform optimally across the network.
Types of Cisco SD-WAN Policies
Let’s explore the different types of policies within the Cisco SD-WAN framework:
- Centralized Policies (vSmart Policies):
- These policies are configured centrally using the vManage Policy Wizard GUI.
- When applied, they are pushed via NETCONF transactions to vSmart controllers.
- From vSmarts, these policies either filter/alter the routing updates or sent to defined Edges.
- Localized Policies (Edge Policies):
- Localized policies are provisioned either:
- Locally through the CLI on the SD-WAN Edge devices.
- Via a Cisco SD-WAN vManage device template.
- When applied, they are pushed directly to Edges.
- Localized policies impact routing decisions within the site-local network where the device resides.
- Localized policies are provisioned either:
Diagram for SD-WAN Policies Types
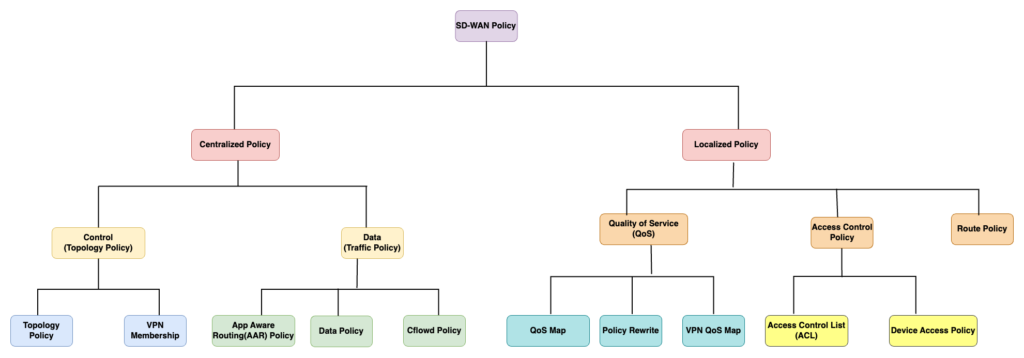
Centralized Policies Types:-
Control Plane Policies:
- Control/Topology Policies: These policies influence the propagation of routing information in the control plane. They allow for preferences between sites, enabling specific destinations to be prioritized over others (or for default routing). Additionally, they control which sites can directly establish tunnels across the fabric.
- VPN Membership Policies: These policies restrict the distribution of routing information related to specific VPNs. For instance, they might be used in guest segments where Internet access is allowed but site-to-site communication is restricted.
Data Plane Policies:
- Centralized Data Policies: These policies directly impact traffic forwarding in the data plane. They serve as a flexible form of policy-based routing, commonly used for tasks like enabling Direct Internet Access (DIA) for specific applications, network service insertion, and data plane manipulations (such as packet duplication and Forward Error Correction).
- Application-Aware Routing Policies: These policies ensure that a specific class of traffic consistently travels across a WAN link that meets a minimum service level agreement (SLA).
- Cflowd Policies: A specialized type of centralized data policy, Cflowd policies specify the destination for exporting flow records. This allows flow information to be analyzed on external systems.
Localized Policies Types:-
- QoS (Quality of Service) Policy: QoS policy is used for classification, scheduling, queueing, shaping and policing of traffic on the Edge router interfaces. This feature help in minimizing the delay, jitter and packet loss of critical application flows as per business requirements.
- Access Control Policy: Cisco SD-WAN provide option to configure ACL on Edge routers to filter traffic based on various parameters like source/destination IP, protocol or application type. Additionally, Cisco SD-WAN ACL provide option to mark/remark traffic for QoS purpose. Note, SD-WAN IOS-XE routers also provide option to configure traditional ACL along with SD-WAN ACL. The main difference between SD-WAN ACL vs Traditional ACL is mark/remarking capability of SD-WAN ACL.
- Route Policy: SD-WAN Route policy are uses for manipulating routing information in OSPF, BGP etc. These can be used for Route filtering, Changing metrics or metric type, Adding community attribute, modifying AS-path information etc.
SD-WAN Policies order of operation
Here is order of operation analogy for various policies.

Further Readings – Cisco Document on SD-WAN Policy Overview
